Encouraging brands to embrace digital marketing opened the doors for new opportunities and success, however, it also brought along a new set of challenges, one of those being a constant flood of marketing industry jargon.
In this blog, we will help you cut through the clutter and provide basic digital marketing terms you should focus on when building a strategy that will help you and your business succeed.
What is Digital Marketing – And Why Should You Care?
Marketing is everywhere, but when people think of it, they often think of billboards, magazines, television commercials, and even ads on the radio.
These are what we refer to as traditional marketing techniques. However, like most things, as the world has evolved, marketing has too.
Digital marketing is the promotion of brands to connect with potential customers using the Internet or other forms of digital communication.
According to the Pew Research Center, three in ten U.S. adults claim they are “almost constantly” online. This explains why businesses are choosing to focus on digital marketing rather than traditional techniques. Using the Internet allows businesses to reach more customers in a shorter amount of time and with less effort. In addition, digital marketing is known to be more cost-effective.

Digital Marketing Key Terms
For brands to get the most out of digital marketing services they need to have a basic understanding of digital marketing terminology and the ability to differentiate these terms with buzzwords.
Buzzwords are words or phrases that are trending during a certain period. These words, or jargon, won’t have the same effectiveness as those that experienced marketers use and know.
Below, we’ve broken down some important digital marketing terms to start with as you build your knowledge.
Organic
When it comes to digital marketing terminology, you should know the three primary terms marketers will often use when they are discussing how to drive traffic (a term we will cover below) and gain leads. The first term is organic.
If someone finds your site on a search engine without clicking on an advertisement or other type of promotional content, it is considered organic traffic.
This is a natural way of spreading brand awareness and generating leads. For example, sending out email newsletters, publishing monthly blog posts and social media posts (not advertisements), or other pieces of content that don’t require a set budget.
Paid
The second way to drive traffic and gain leads is through paid marketing techniques. These include advertisements or campaigns that require a daily or lifetime budget. For instance, running monthly social media advertisements on LinkedIn.
Typically, businesses will find that paid campaigns perform better than posting organically. This is often because platforms will allow you to use detailed targeting. However, having a balance of both paid and organic marketing is beneficial since you’re likely to reach more people overall.
Referral
If a user finds your site without organically searching or clicking on a paid ad, it’s known as referral traffic. When someone visits a hyperlink from a social network or website and ends up on your site, search engines can recognize this as a referral visit.
Many businesses will also use UTM codes to track exactly where these users are coming from. Doing this allows you to see which social networks or sites are bringing in the most traffic.
Traffic
As promised above, the next digital marketing term everyone in the industry should be aware of is “traffic”. Simply put, traffic refers to the number of users who have visited your website or social media profiles.
This metric is crucial for every brand, but especially those who are trying to increase brand awareness. It’s important for marketers to not only see that traffic is coming through but also to locate where users are coming from.
For example, in Google Analytics, you’re able to identify if a user came to your site organically (in a search engine) or through a paid ad. Determining this will help you build a marketing strategy that is aligned with your overall goals.
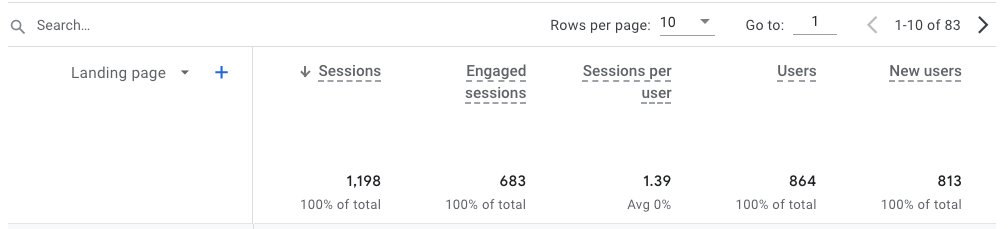
Session
As we mentioned previously, you can track the traffic for your site in Google Analytics, but to do that you need to understand another key digital marketing term known as sessions.
Every time a user visits your site, they start a session, and after 30 minutes of inactivity, the session ends. This means if someone is on your site for even a second, they are counted as a session. In the same respect, if a user leaves your site and comes back a few hours later or the next day, it’s counted as a new session.
However, most businesses don’t simply want to know if people are visiting their site, but also how long they’re staying. This is where engaged sessions come into play. When a user stays on your site for more than 10 seconds, completes a conversion (we’ll discuss more about this below), or has at least 2 pageviews, it’s considered an engaged session.
While sessions alone can be helpful, engaged sessions are arguably more important because they show businesses that users are absorbing information on their site and therefore becoming one step closer to becoming leads or customers.
Lead
The primary goal of any company or business is to gain customers and increase revenue. Marketers can assist them in this by creating strategies to bring in new leads. A lead is any user that shows interest in a brand, product, or service.
Depending on the company itself, the quality of leads may vary, however, for the most part, a qualified lead refers to someone who fills out a contact form, requests a quote, signs up for a trial, or takes any other action that pushes them closer to becoming a customer.
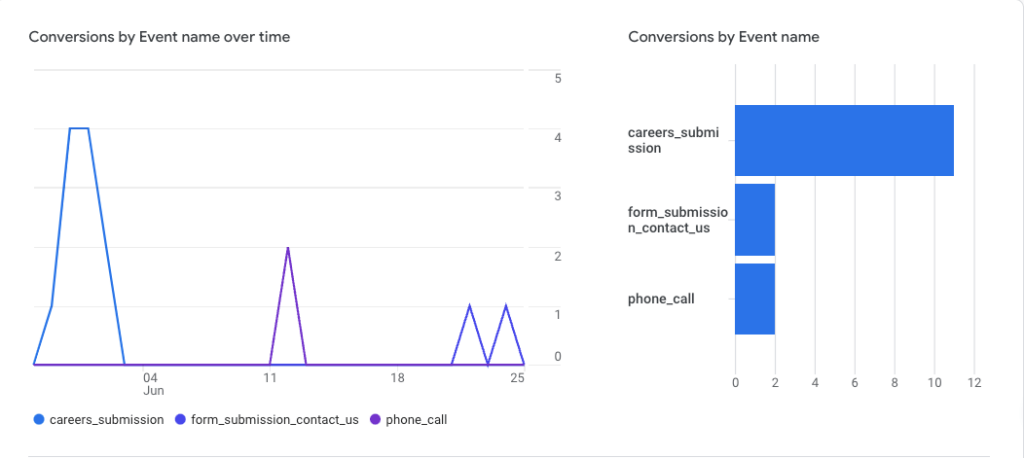
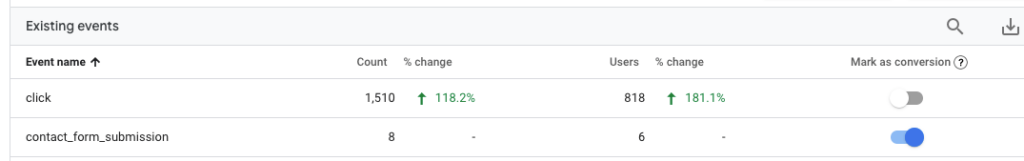
Conversions
We’ve mentioned the term conversions a few times, which is appropriate because, in many ways, these are some of the most valuable metrics in digital marketing. When creating a marketing strategy, marketers will break down a number of actions they want users to take.
Conversions can vary in importance, what the business is trying to achieve will greatly impact what types of conversions digital marketers decide to set up.
This could be viewing a landing page, clicking a contact button, or downloading a file, a conversion happens whenever a user completes a desired action.
Call to Action (CTA)
A digital marketing term you’ll hear frequently is a call to action or CTA. This refers to the next step a marketer wants the audience to take to push them further through the sales funnel.
Usually appearing at the end of a content, ad, or email, a good CTA will be clear and concise. Often CTAs will include a direct link for a user to click on.
Whether it leads to a contact form, product page, or another resource, the goal of a CTA is to keep the reader engaged and interested in a service or product.
A/B Testing
Also known as “split testing”, A/B testing is a digital marketing term that describes the process of comparing two variables to determine which performs better.
For example, if you are experimenting with email headlines and want to see what is more effective, you can send out two emails that have the same copy, and list but contain different headlines.
Based on how each performs, you can determine which headline is stronger. This is a technique digital marketers use in several areas to improve conversion rates and optimize their content.
Key Performance Indicator (KPI)
Commonly referred to as KPIs, key performance indicators, are how marketers measure their progress against an objective.
There are two types of indicators to be aware of when creating goals: lagging and leading. Lagging indicators assess the current state of business performance while leading indicators work to predict future success.
It’s important to take into account both types because while lagging indicators aren’t helpful with making ongoing adjustments, they can help you shape your goals which should be based on leading indicators.

Tactical Digital Marketing Terms
Now that we’ve covered some of the basic digital marketing terms, it’s time to dive into the specifics.
Generally speaking, 4 main types of services go hand-in-hand with digital marketing. In the following sections, we’ll explain what these are and what terms are specific to the work they do.
Basic SEO Terms to Know
Search engine optimization, or SEO, refers to the process of improving a website to increase its visibility in search engines, like Google or Microsoft Bing. The main goal of SEO is to increase traffic and attract users who will become leads, customers, or an audience that continues to come back.
Title Tag– The name of a specific web page. These will appear at the top of a web browser or in search engine results.
Search Engine Results Page (SERP)– The page of results users see when they type a word, phrase, or query into a search engine.
Meta Description– Tied to a specific page, these are used to describe web pages and encourage users to click on links in the SERP.
Keyword– A word or phrase a user types into a search engine to find what they are looking for. Using keywords in titles, headings, and body of texts will help improve a page’s ranking.
Ranking Factors– The criteria applied by search engines when evaluating web pages to decide where each page should fall on the SERPs.
Events– A metric that records a specific user interaction or occurrence on a website, for example clicking a button, submitting a form, downloading a file, and more.
Conversion Rate– Measures the number of users who converted (taken action) as a percentage of the total number of users who visited a site. This can be calculated by the total number of conversions divided by the total number of clicks.
Basic Content Marketing Terms to Know
Content marketing involves the creation and distribution of valuable and relevant online material that is intended to promote a brand as well as spark interest in its products or services. These materials include a wide variety of content pieces from blogs to whitepapers.
Buyer Persona– A detailed description of a business’s ideal customer, outlining their customer’s desires, pain points, demographics, etc.
Bounce Rate– The percentage of users who enter a website and leave rather than continuing to browse pages within the same site.
Landing Page– Any page on a website where traffic is sent to prompt a specific action or result.
Copywriting– The process of creating content for web pages, blogs, or social media posts to convert users.
Customer Journey– An outline of the different steps users will take to become qualified leads, customers, or clients.
Sessions Per User– The average number of sessions each user engages on a specific site or application. This can be calculated by dividing a site’s session count by its user count.
Basic Email Marketing Terms to Know
Email marketing helps you reach potential customers, increase brand awareness, build customer loyalty, and promote other marketing efforts. The messages in emails can include valuable content, updates, coupons, or exclusive offers.
Email Automation– An email marketing strategy that sends specific messages according to certain triggers or scheduled times.
Dynamic Content– Email content that changes based on a user’s data, preferences, and behaviors to show them specific messaging.
List Segmentation– A process of breaking down email lists into smaller segments to create personalized messages.
Email Deliverability– The ability to successfully deliver emails to users’ inboxes.
Drip Campaign– A series of automated messages or emails sent to leads regularly and over a scheduled period.
Open Rate– The number of email recipients who opened an email.
Click Rate– The percentage of people who opened an email and clicked on a link or ad within the email. This can be calculated by dividing the number of emails clicked by the number of emails sent.
Click-To-Open Rate– The percentage of people who opened an email and then clicked a link within that email. This can be calculated by dividing unique email opens by unique email clicks and then multiplying by 100.
Basic Social Media Marketing Terms to Know
Social media marketing is the use of social media platforms to interact with customers to build brands, increase sales, and drive website traffic. Social media can be shared organically and can be used for paid advertising.
Impressions– The number of times content has been shown on the feeds of social media users.
Engagement Rate– A metric that shows how much interaction a social media post or ad campaign earns from users. This can be calculated by dividing the total engagement by total followers and then multiplying by 100%.
Conversion Rate– The percentage of users who follow through a social media post or ad’s call to action.
Cost Per Click (CPC)– A metric that determines how much advertisers pay for social ads based on the number of clicks the ad receives. This can be calculated by dividing the advertising cost by the number of clicks generated by the advertisement.
Click-Through Rate (CTR)– The number of clicks an ad receives divided by the number of times an ad is shown.

Staying educated about basic digital marketing terminology is beneficial for businesses because it gives them the ability to not only understand what other competitors are doing online but also the chance to create a marketing strategy that will put them ahead of their competition.
With this knowledge, you have the opportunity to build relationships with like-minded people who can help tell your brand’s story and achieve your goals.
Interested in learning more about digital marketing? Browse our case studies to see some of our recent marketing projects.
This blog was originally published on March 30, 2021, and updated on November 1, 2023.